USB 3.0 hub is known for its compatibility with older USB versions like USB 2.0 and USB 1.1. You can comfortably use a USB 3.0 hub in an older version port. The only downside is that the device will only be running at the speed of the older version of the technology.
So, if you are plugging a USB 3.0 hub into a USB 2.0 port, it is better to expect the device to operate and transfer data only at the speed of the USB 2.0 technology. Let us have a deeper look at this situation and find the essential differences between various USB hubs and ports.
Will a USB 3.0 Hub Work on a 2.0 Port?

According to expert opinion and available data, a USB 3.0 hub does work on a USB 2.0 port. USB 3.0 is an upgraded technology of USB 2.0. Usually, people leave the assumption that USB 3.0 does not exhibit backward compatibility. That is, they are not compatible with their previous technologies.
But the fact is different. USB 3.0 exhibits high compatibility with most of its previous technologies like the USB 1.1 and USB 2.0. The only issue that happens with these combinations is that the operation of the device tends to slow down a bit. The device would only work at the speed of the older technology, not at the USB 3.0 speed.
The reason for this essential slowdown is the number of cables inside the USBs. In USB 2.0, the number of cables used for data transfer and other operations is four. But a USB 3.0 version hub contains nine wires.
There are not enough wires with the 2.0 version to connect to the whole of 3.0, so the operation and data transfer only occur through the available four-wire combinations. This is why the system or device gets slowed down to the 2.0 technology’s speed.
Are USB 2.0 and 3.0 Ports the Same Size?
No, USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 ports are not always the same size. While the standard Type-A USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 ports are the same size, other types of USB connectors such as Micro-B and Type-C can differ in size and shape between the two standards.
- Type-A: Both USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 Type-A ports are the same size, and a USB 2.0 Type-A plug will fit into a USB 3.0 Type-A port and vice versa. The USB 3.0 Type-A port usually has a blue interior to distinguish it from the USB 2.0 port.
- Micro-B: The USB 3.0 Micro-B connector is wider than the USB 2.0 Micro-B connector. This is because the USB 3.0 standard includes more pins to support higher data transfer rates.
- Type-C: This is a relatively new type of connector that is universal and can support both USB 2.0 and USB 3.0 (as well as USB 3.1 and USB 3.2) standards. However, the port itself is quite different from Type-A and Micro-B ports.
- Mini-B: This connector is mostly found in older devices and is usually associated with USB 2.0. USB 3.0 devices generally do not use Mini-B connectors.
So, while some ports and connectors may be the same size, it’s not a rule that applies across all types of USB connectors.
Different USB Connectors
Before proceeding to check the compatibility chart of all USB ports and connectors, it is essential first to understand the various options available in the world of USBs.
USBs are differentiated based on two criteria.
1. Type
The type of a USB connector refers to its shape. It plays a major role in deciding the compatibility between a USB hub and a USB port.
2. Version
Version refers to the technology used in the USB device. The version is the deciding factor regardinga USB device’s operational speed and data transfer capabilities. Many USB versions exhibit high compatibility with their older and newer versions.
USB Compatibility Chart
As mentioned before, USB connectors and ports are divided based on their technology versions and types. So, not all USB hubs would be compatible with every other USB port.
The following USB compatibility chart explains which hubs are compatible with which ports and vice versa. It will be extremely helpful while choosing and using any USB device.
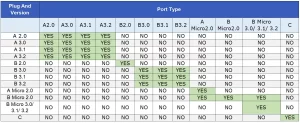
USB 3.0 vs. USB 2.0: A Comparative Overview
Speed
- USB 3.0: Offers transfer rates of up to 5 gigabits per second (Gbps), making it significantly faster for data transfer.
- USB 2.0: Has a maximum data transfer rate of 480 megabits per second (Mbps), considerably slower compared to USB 3.0.
You may also like: Are SATA 3 cables transfer speeds faster than USB 3.0?
Power Efficiency
- USB 3.0: More power-efficient because it offers better power management features and can provide more power to connected devices if needed.
- USB 2.0: Generally less efficient in power management, which can be an issue for battery-powered devices.
Cable Length
- USB 3.0: Typically limited to shorter cable lengths compared to USB 2.0, due to its higher data rates.
- USB 2.0: Supports longer cable lengths, giving it a slight advantage for some applications.
Compatibility
- USB 3.0: Backward compatible with USB 2.0, meaning you can plug a USB 2.0 device into a USB 3.0 port.
- USB 2.0: Can be plugged into a USB 3.0 port, but you won’t benefit from the increased speed of USB 3.0.
Color Coding
- USB 3.0: Ports and plugs are generally blue, making them easier to identify.
- USB 2.0: Typically not color-coded or comes in a variety of colors, making identification less straightforward.
Cost
- USB 3.0: Generally more expensive due to its higher performance.
- USB 2.0: More affordable but offers less speed and efficiency.
Both USB 3.0 and USB 2.0 have their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. USB 3.0 is the clear winner if speed and efficiency are paramount, whereas USB 2.0 might be more suitable for simpler tasks and longer cable requirements.
You may also like: How USB 2.0 to USB 3.2 Gen 1 Header Adapter Works?
What is the Main Difference Between 2.0 and 3.0 USB Hub?
The significant differences between 2.0 and 3.0 USB hubs are as follows.
- USB 3.0 has nine connector wires, but USB 2.0 only has four of them.
- USB 3.0 has a blue color inside, whereas USB 2.0 has a black or white color inside.
- USB 3.0 provides up to 5 Gbit per second transfer rate, whereas USB 2.0 only features a 480 Mbps transfer rate, which is about ten times slower than the former.
- USB 3.0 devices are relatively more expensive than USB 2.0 devices.
- Regarding power delivery and power management, USB 3.0 is much more advanced than USB 2.0.
- USB 3.0 maintains a two-way communication, whereas USB 2.0 maintains a one-way communication.
- USB 3.0 has a cable of about three meters long, while USB 2.0 has up to five meters of cable length.
- USB 3.0 provides up to 900 mA power, while USB 2.0 provides about 500 mA power.
USB 3 Backwards Compatible USB 1
USB 3 devices usually exhibit good physical compatibility with their previous versions of hubs like USB 1.1 and USB 2.0. All of them use similar physical connectors and use a similar basic protocol.
However, it is essential to note that even though USB 3 is physically compatible with USB 1.1, the speed of the connection will not be up to the regular USB 3 standards. The connection will function only in the USB 1.1 hub’s speed standards.
Conclusion
The USB standards have developed over time. While many USB hubs maintain physical compatibility with many of their previous versions, only the latest versions provide advanced speed and operational efficiency. According to the experts, connecting between the same version and type of USB is always advisable to get the best data transfer rate and performance.
